"Business Process as a Service" (BPaaS)
"Business Process as a Service" (BPaaS) is considered as a new paradigm that introduces the next abstraction from IaaS, PaaS, SaaS towards domain specific BPaaS.
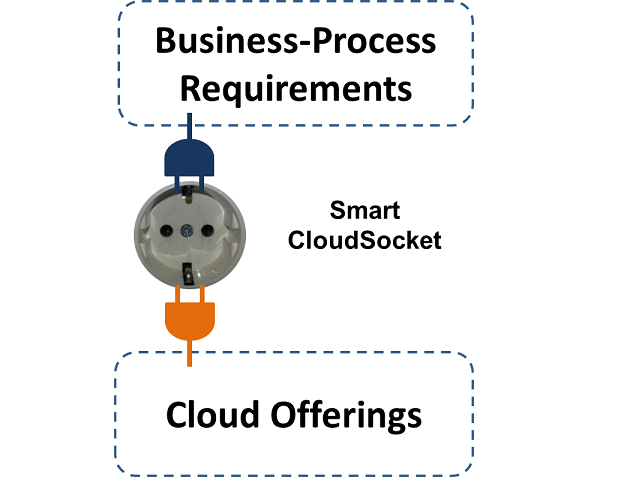
Hence, BPaaS is not seen as a technical combination of SaaS, but is seen as a mediator between IT-agnostic business users and Cloud computing.
Business process management based on modelling is a well established approach, hence CloudSocket uses business process models as the source of IT-Cloud requirements.
This projects puts forth the idea of a “hybrid process” modelling framework applying well-known techniques for semantic, rule-based inference, meta modelling and
knowledge management techniques to bridge the gap between business needs and the use and exploitation of Cloud resources and components.
The proposed framework implements a layered approach for managing the complexity of bridging the semantic distance from business process to workflow
configuration of BPaaS in the Cloud.
The CloudSocket Challenge
The CloudSocket Challenge:
Business Process Model based approaches have two categories:
- Business Process Models can be used for configuring software but also act as a basis of organisational knowledge.
- Business Processes are interpreted as the know-how platform of an organisation serving both (a) human and (b) machine interpretation.
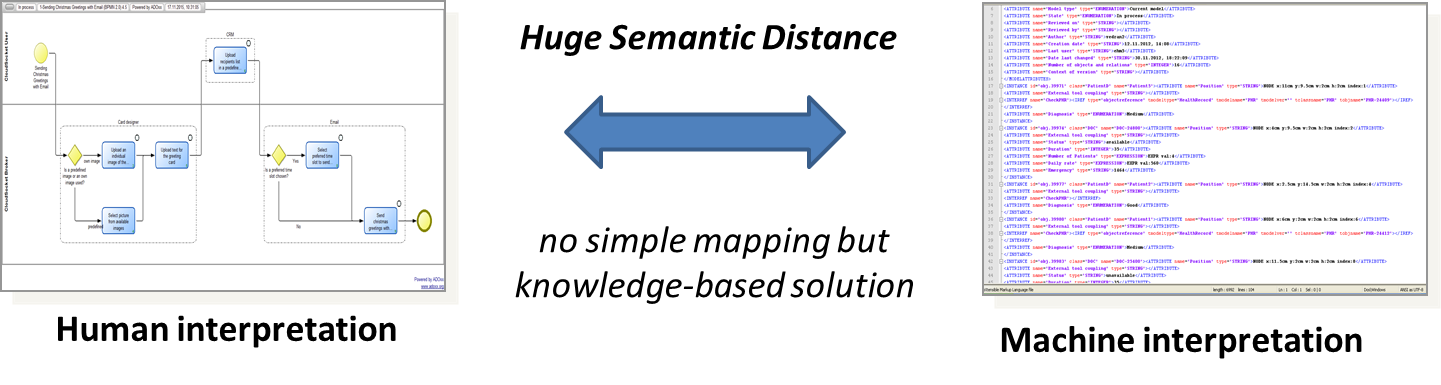
CloudSocket addresses the latter interpretation of the business process and hence addresses semi-formal, graphical representation that are intended to be read by human and not by machines.
This results in the huge challenge to bridge the semantic distance from human-interpretable business process models that are intended to be read by users towards workflows and corresponding deployment information that is intended to be automatically processed by machines.
APQC Classification of Business Processes
The term business process and workflows are often confused. For a clear spearation of terms please visit D2.2.
In order to underline the nature of the business process as a potential know-how platform of the organisation and not a software orchestration, some categories of the APQC framework are shown in a BPaaS Designer. Reading those categories should stress the fact that human users are reading the graphical representation in order to better understand the operation of the organisation.
CloudSocket uses this instrument, by better explaining the added value of cloud computing for the organisation.
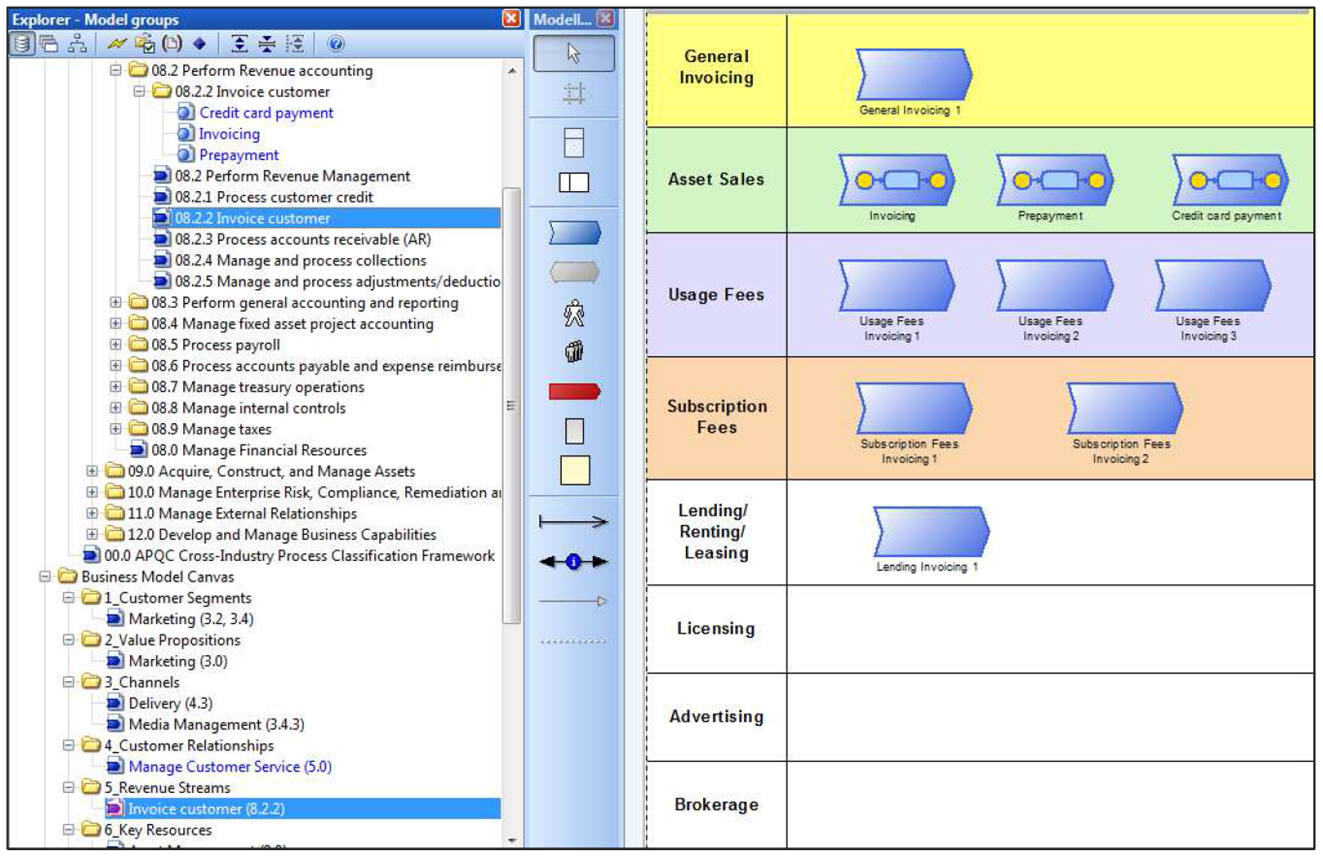
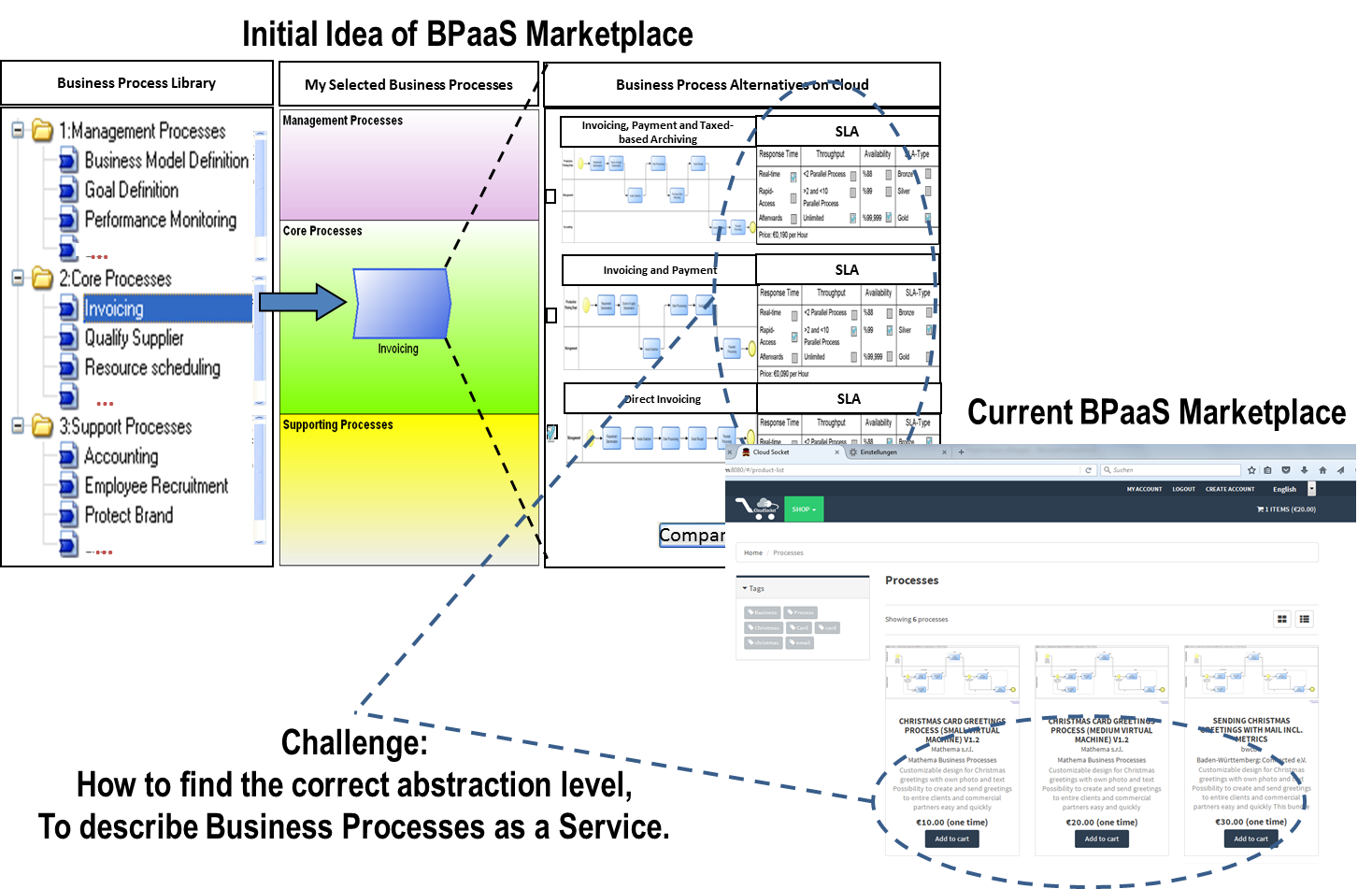
BPaaS offerings in the Marketplace
In order to target CloudSocket customers with BPaaS offerings, the CloudSocket Broker is creating a marketlace. The top figures indicates the initial mockup of a potential marketplace, with the APQC classification on business processes on the left side, and after selecting a concrete business process category a list of business processes on the right side.
The different business processes are compared according cloud characteristics.
Current BPaaS marketplace is depicted as the right lower figure, showing three BPaaS offerings. Currently the technical properties are presented as text to enable the comparison between the BPaaS offerings.
The major challenge is to find the correct abstraction level to describe Business Processes as a Service, so on the one hand they provide useful information to the business user to select a BPaaS, on the other hand the information is reasonable detailed for technical staff to operate the corresponding workflow.
Business Process Management System Paradigm (BPMS)
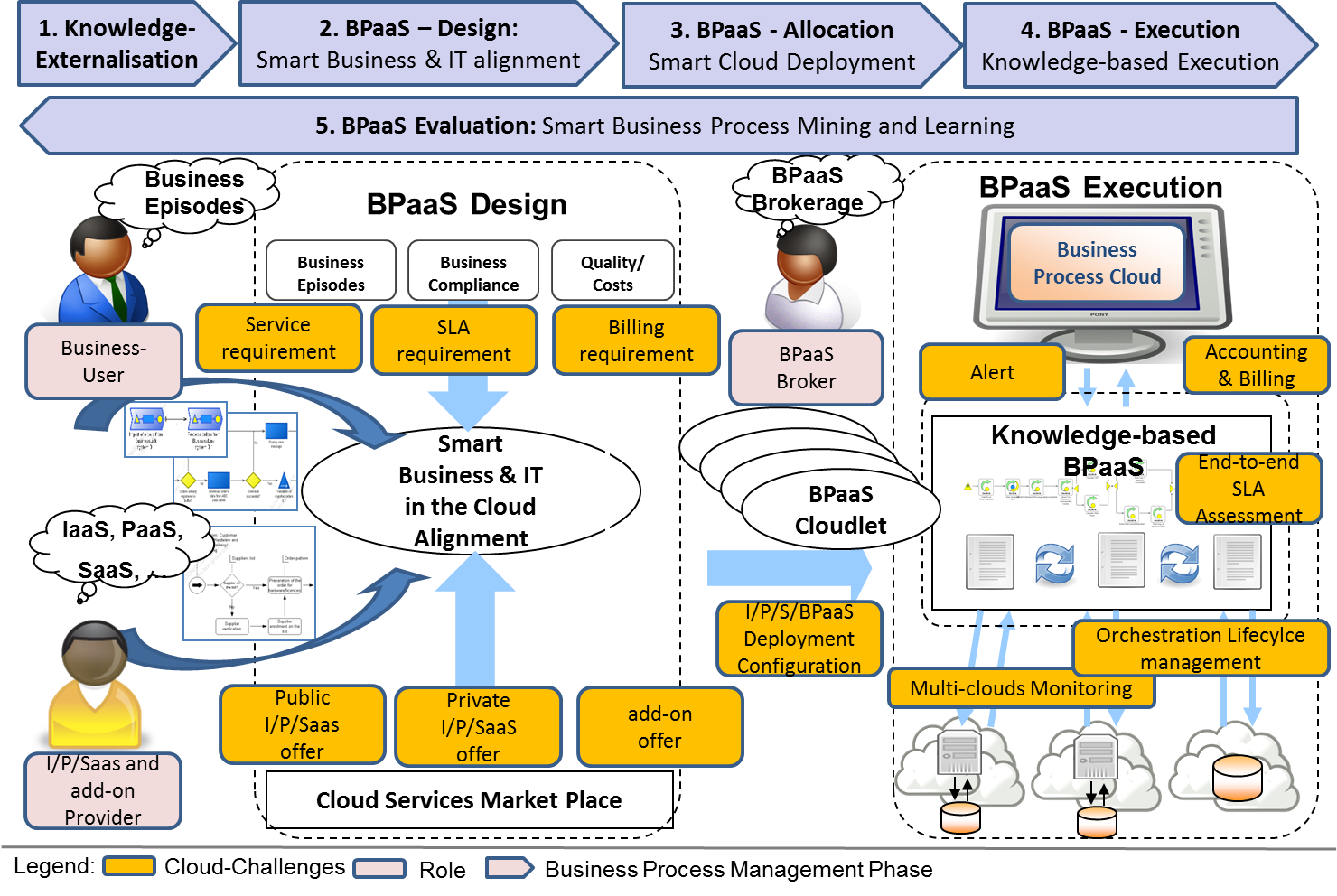
The BPMS paradigm indicates the management of business processes in five phases, the strategy phase, the design phase, the allocation phase, the execution phase and finally the evaluation phase that feedbacks to aforementioned phases introducing a cycled approach.
In order to map the BPMS approach with cloud computing challenges, each relevant phase is maped with a corresponding BPaaS environments that addresses the respective cloud challenges.
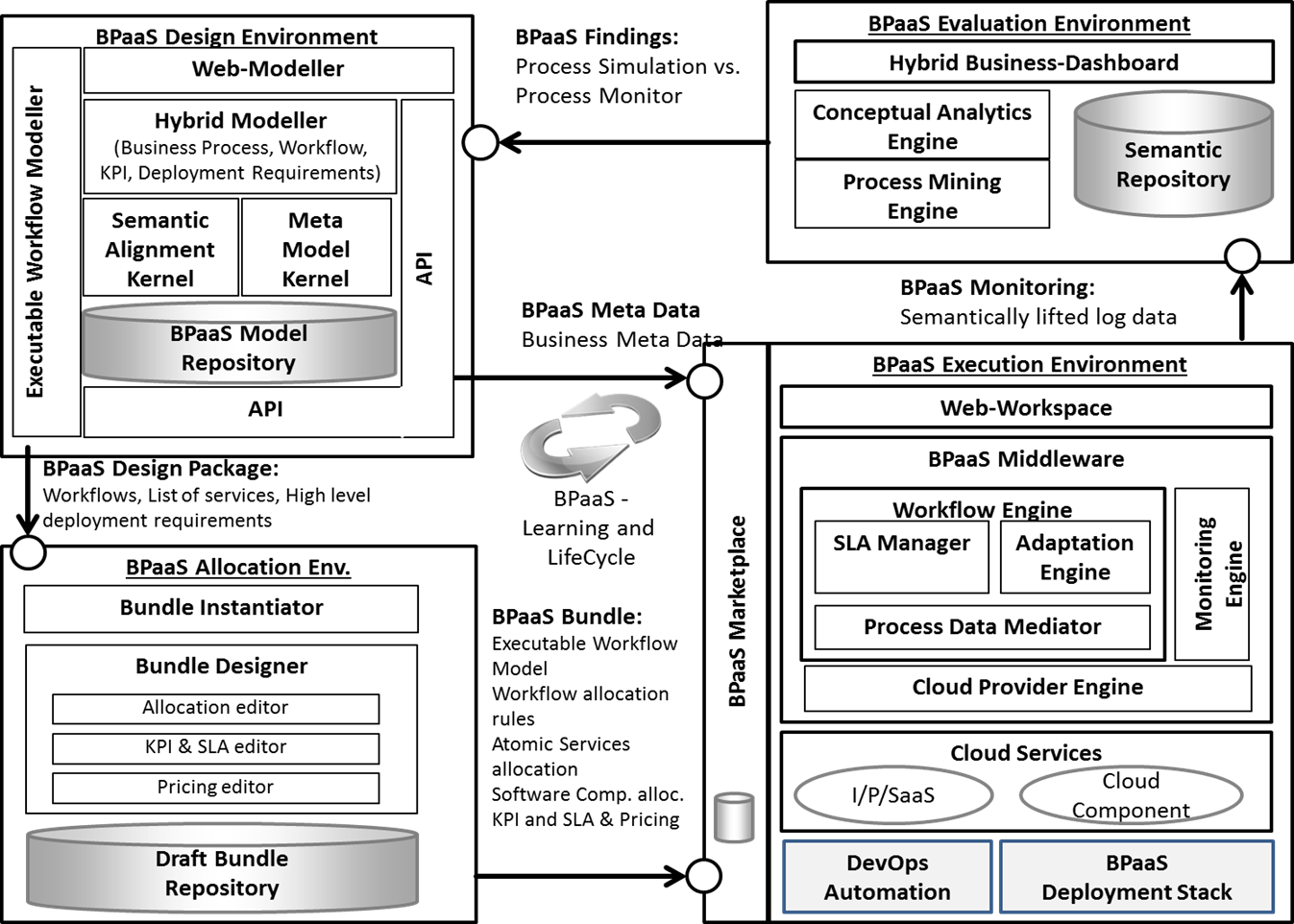
This overview indicates that the BPaaS Design environment deals with the smart business and IT alignment. As business process models are used, this means that such business process models are extended with semantic, rules and cloud specific extensions, to enable rule inference, pattern matching and hence smart alignment of domain specific business process models and cloud-specific IT models.
The BPaaS Allocation Environment uses the aligned BPaaS Design package and enriches it with deployment and marketplace relevant information. Currently the CAMEL notation is used to describe the deployment of the business process. Research will also introduce a semantic lifting and smart support to find approapriate cloud offerings.
The BPaaS Marketplace and Execution Environments deals first with the offering of BPaaS in the marketplace and second with the deployment of the BPaaS in a multi-cloud execution environment. As the focus of CloudSocket is the management framework supporting the CloudSocket Broker, the cointinues monitoring of Key Performance Indicators (KPI) of the operating business process is important. KPIs are separated in different concerns, ranging from business level, allocation level and operation level. Special monitoring services are used to identify the relevant measures.
The BPaaS Evaluation Environment collects all aforementioned KPI measures and abstracts the raw sensor data back into semantically enriched business process indicators. This so-called conceptual analysis translates semantic queries with business process properties. Finally this environment displays the evaluation results in a business cockpit, supporting the CloudSocket Broker in the management of BPaaS offerings.
In the following, the core innovaiton items are mentioned:
- Business Process Requirement Definition: Business process models to define requirements.
- Domain specific Cloud Offering Definition: Semantics considering technological and also the domain specific business dimension.
- BPaaS orchestration: Workflow orchestration of cloud services in multi-clouds.
- Adaptive Orchestration in a Multi-cloud Environment: Business rules are translated into deployment rules.
- Cloud Service and Cloud Component Interoperability: Developing interfaces and adapter to existing cloud services is a technological necessity.
- Business Process based Billing and SLAs: Monitoring across cloud services to enable business process relevant billing.
- Smart Service Management and Monitoring: Abstraction back from technical log mining to domain specific business dashboards.
Research Findings are published in D3.1.